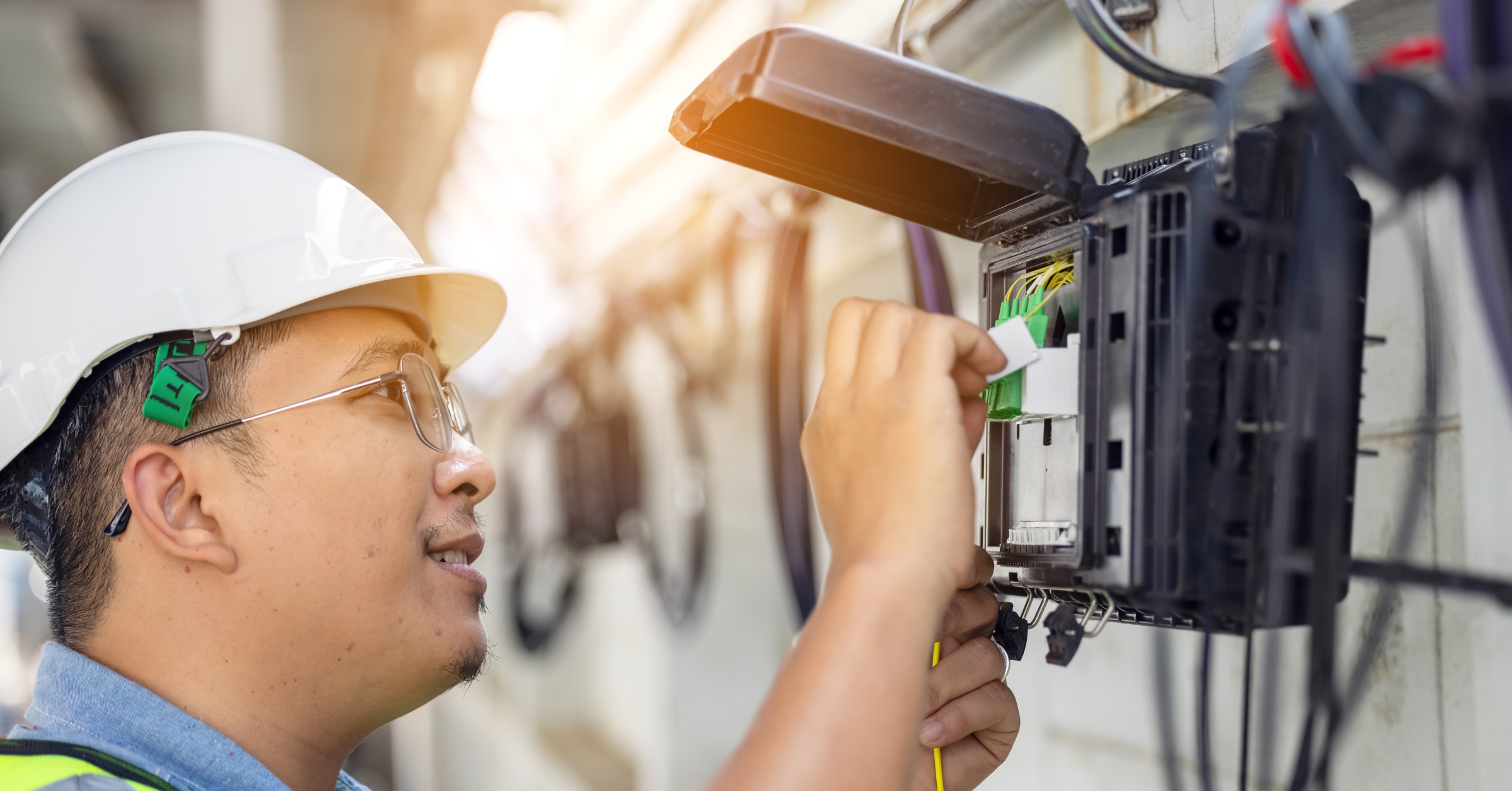
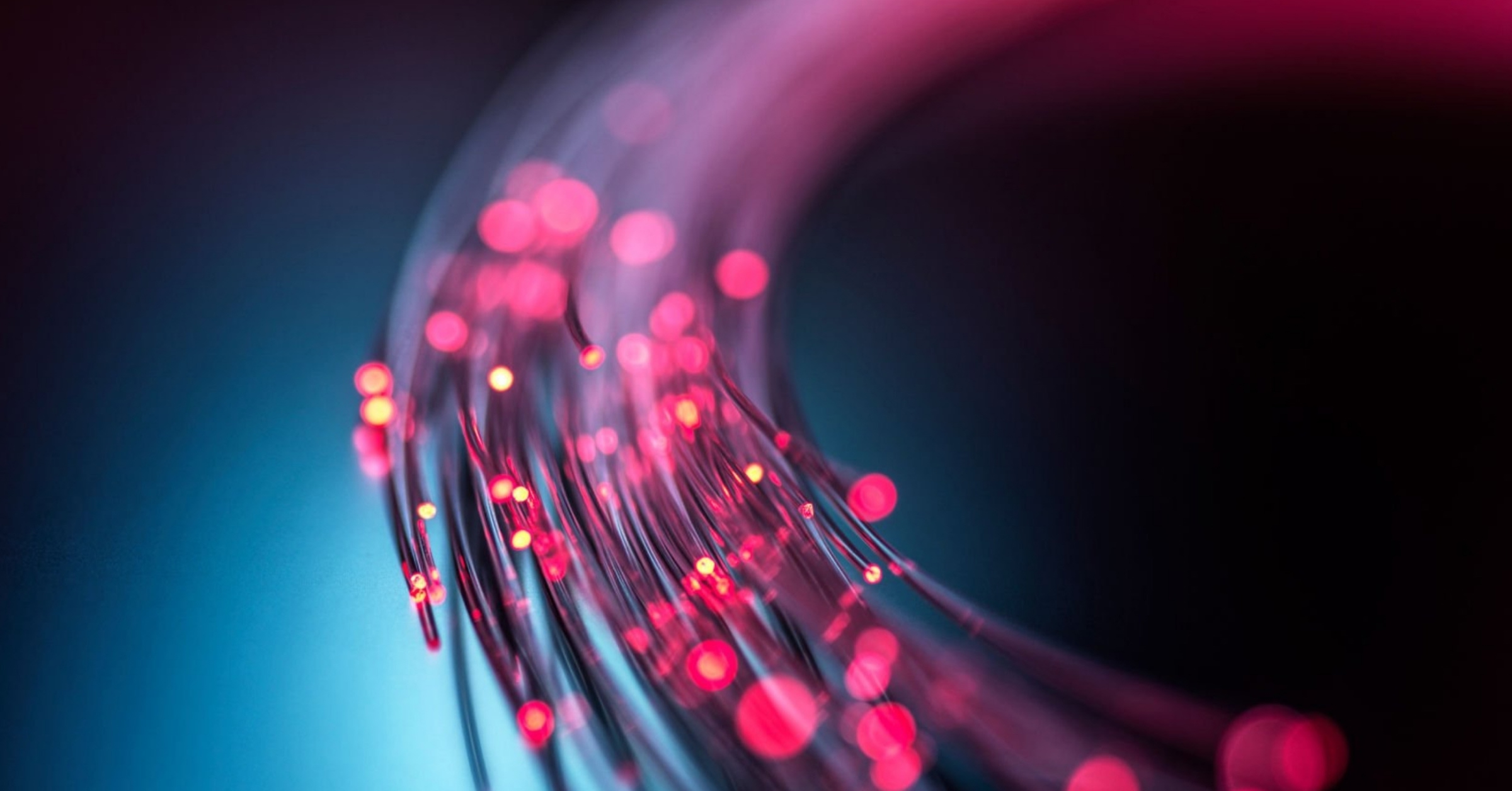
Ultra-fast.
Sustainable.
100% fibre-optic.
Check if your address is covered.
Choose fibre-optic speeds up to 10 Gigabits.
The ultra-fast network for home, companies, and public administrations
Internet without limits.
Enjoy uninterrupted streaming and gaming, a stable and secure connection, and stress-free smart working.
Give your business new momentum.
Stable, high-speed connection for smooth video calls, fast uploads, and smart business management. Stay focused, always connected.
Uncompromising top performance.
Reliable and fast networks to ensure seamless productivity, collaboration and innovation. Drive your company’s future at top speed.
Efficiency and digital innovation.
Enhance public services with ultra-fast connectivity. Faster processes and efficient remote work, powered by pure fibre-optic connectivity.
Tailor-made solutions to grow together.
Access reliable, scalable fibre-optic infrastructure, perfect to offer the best to your customers and expand your business opportunities.
Open Fiber Partners
Join our network and choose from over 300 Operators, quality services and tailored offers.
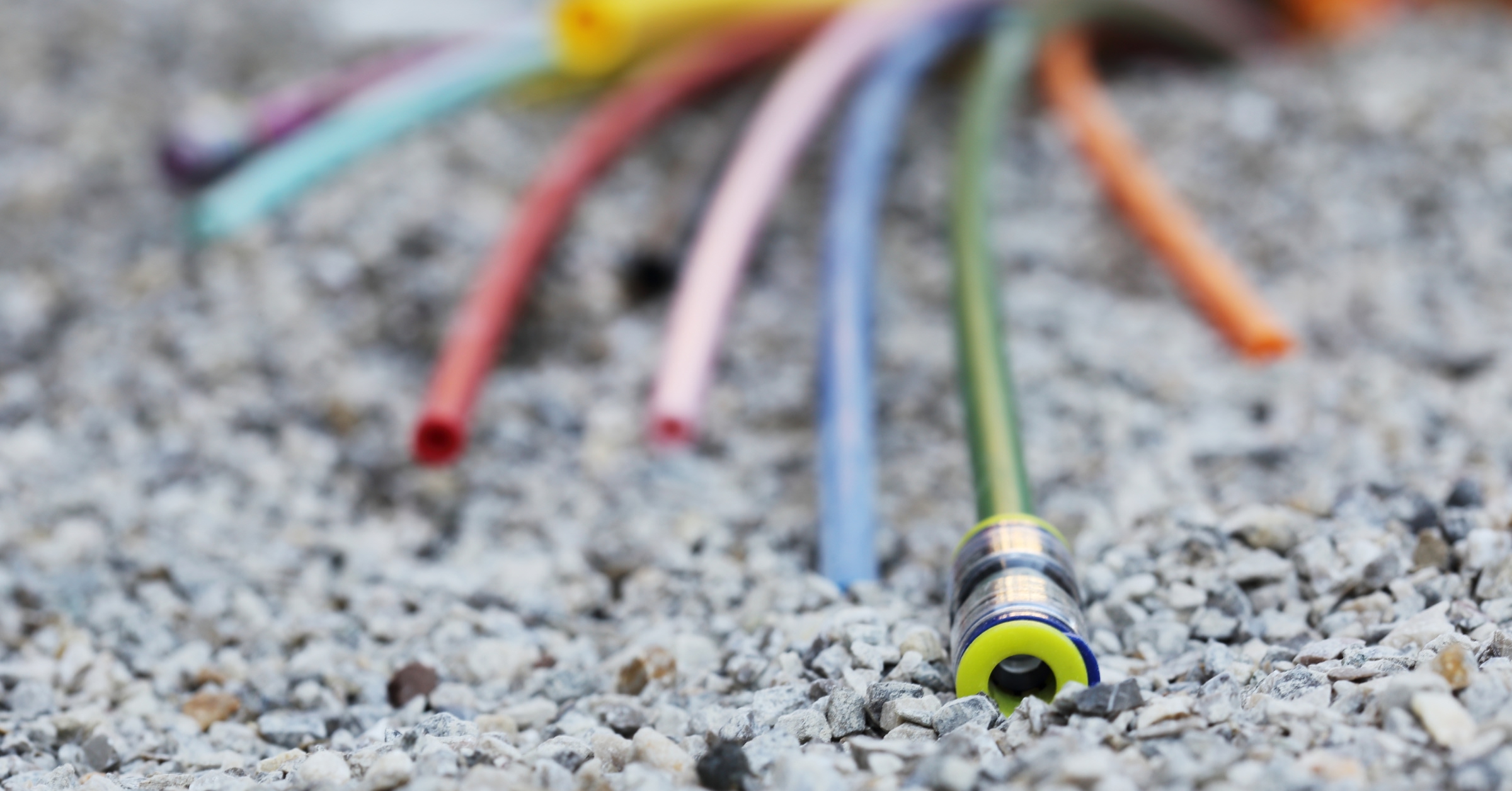
Bringing optical fibre to the whole country
We connect cities, suburbs and rural towns through an ultra broadband network infrastructure entirely based on FTTH technology.
Data updated 31 October 2025
*Municipalities where the fibre optic network is ready for service sales by Partner Operators.
**Property units passed by the fibre optic network and ready for connectivity service activation via Partner Operators.

Growing together through sustainable choices
We adopt technological, industrial and social development strategies that respect the environment.
Get connected with ultra-fast fibre!
Check if your address is covered by Open Fiber’s 100% fibre-optic network!